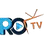Exploring the world of exterior wall insulation systems for cold climates, this article delves into the importance of proper insulation to combat the harsh cold, highlighting common materials used and the benefits they offer.
Overview of Exterior Wall Insulation Systems
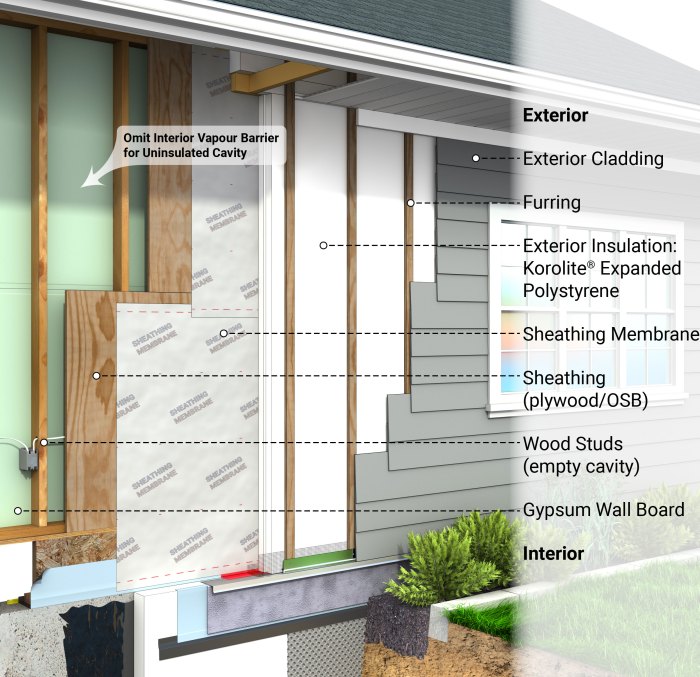
Insulating exterior walls in cold climates is essential to maintain indoor comfort, reduce energy costs, and increase the overall efficiency of a building. By adding insulation to the exterior walls, the heat loss through the walls is minimized, creating a more stable and comfortable indoor environment.Common materials used in exterior wall insulation systems for cold climates include:
Fiberglass
A popular choice due to its affordability and effectiveness in preventing heat transfer.
Foam board
Provides excellent insulation and can be easily installed on the exterior walls.
Mineral wool
Offers great thermal performance and fire resistance, making it a suitable option for cold climates.The benefits of using exterior wall insulation systems in cold regions are numerous:
Increased energy efficiency
Insulation helps reduce heat loss, leading to lower heating costs.
Improved comfort
A well-insulated building maintains a consistent indoor temperature, keeping occupants comfortable.
Reduced environmental impact
Lower energy consumption means reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Examples of Exterior Wall Insulation Systems
- 1. Fiberglass insulation: Lightweight and cost-effective, fiberglass insulation is commonly used in exterior wall systems for its thermal performance.
- 2. Foam board insulation: Provides excellent insulation value and moisture resistance, making it ideal for cold climates.
- 3. Mineral wool insulation: Known for its fire resistance and sound absorption properties, mineral wool is a durable option for exterior walls.
Types of Exterior Wall Insulation Systems
When it comes to exterior wall insulation systems for cold climates, there are several types of insulation materials to choose from. Let's compare and contrast different options and explore the installation process for each type.
Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is a popular choice for exterior walls due to its affordability and effectiveness in cold climates. It is typically installed in batts or rolls and offers good thermal performance.
Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation provides excellent insulation by expanding to fill gaps and cracks, creating a tight seal. While more expensive, it offers superior energy efficiency and can prevent air leakage.
Cellulose Insulation
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper and treated with fire-retardant chemicals. It is a sustainable option that provides good thermal performance and can be blown into wall cavities.
Rigid Foam Insulation
Rigid foam insulation boards are easy to install and provide a high level of insulation. They are moisture resistant and can help prevent mold growth in cold climates.
Innovative and Eco-Friendly Solutions
Some innovative insulation solutions for cold climates include aerogel insulation, which offers superior thermal performance in a thin profile, and sheep's wool insulation, which is a natural and sustainable option.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Exterior Wall Insulation
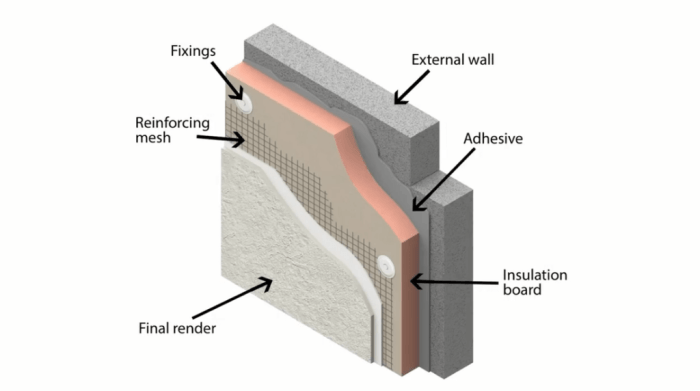
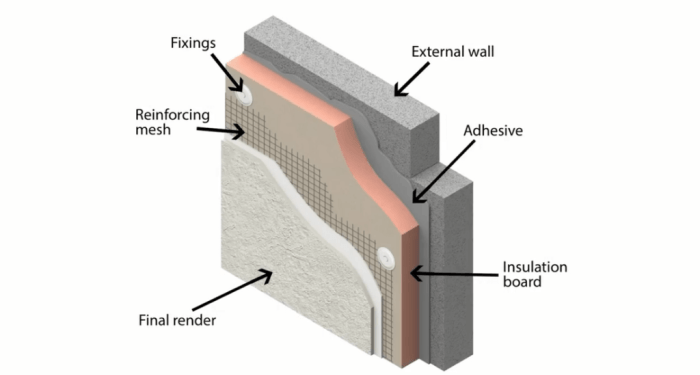
When selecting exterior wall insulation systems for cold climates, several key factors need to be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency
R-Value
The R-value of insulation is a measure of its thermal resistance, indicating how well it can prevent heat transfer. In cold climates, a higher R-value is essential to effectively insulate exterior walls and minimize heat loss. It is important to choose insulation materials with the appropriate R-value to ensure maximum energy efficiency and comfort in your home.
Moisture Resistance
Moisture resistance is another critical factor to consider when selecting exterior wall insulation for cold climates. Insulation materials that are resistant to moisture help prevent mold, mildew, and structural damage caused by water infiltration. It is essential to choose insulation products with proper moisture barriers and ensure proper installation to maintain the integrity of the insulation system.
Durability
Durability is key when choosing exterior wall insulation systems for cold climates. Insulation materials should be able to withstand harsh weather conditions, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to moisture without deteriorating or losing their insulating properties over time. Opt for durable insulation products that can provide long-lasting performance and energy savings.
Building Codes and Regulations
Building codes and regulations play a significant role in determining the type of exterior wall insulation systems that can be used in cold climates. It is essential to comply with local building codes and regulations to ensure the safety, performance, and energy efficiency of the insulation installation.
Be sure to check with your local authorities and consult with professionals to select insulation products that meet the necessary requirements.
Tips for Maximizing Energy Efficiency
- Choose insulation materials with the highest R-value suitable for your climate.
- Ensure proper installation to eliminate gaps or thermal bridges that can reduce insulation effectiveness.
- Consider additional measures such as air sealing and vapor barriers to enhance the performance of your insulation system.
- Regularly inspect and maintain your insulation to ensure optimal energy efficiency and comfort in your home.
Maintenance and Upkeep of Exterior Wall Insulation
Proper maintenance of exterior wall insulation systems in cold climates is essential to ensure their longevity and effectiveness in providing thermal protection to buildings. Regular upkeep helps in identifying issues early on and prevents costly repairs in the future.
Best Practices for Maintaining Exterior Wall Insulation Systems
- Regularly inspect the exterior walls for any signs of damage, such as cracks or gaps, and repair them promptly to prevent heat loss.
- Ensure proper drainage around the building to prevent water infiltration, which can compromise the insulation's performance.
- Trim any vegetation or bushes near the walls to prevent moisture buildup and potential damage to the insulation.
- Consider applying a protective coating or sealant to the exterior walls to enhance their durability and weather resistance.
Common Issues or Challenges with Exterior Wall Insulation and How to Address Them
- Poor installation leading to gaps or voids in the insulation material can result in thermal bridging and reduced efficiency. It is crucial to hire experienced professionals for installation to prevent such issues.
- Damage from pests or rodents can compromise the integrity of the insulation. Regularly inspecting the walls and sealing any entry points can prevent infestations and damage.
Importance of Regular Inspections and Repairs for Optimal Insulation Performance
Regular inspections and timely repairs are vital to maintain the optimal performance of exterior wall insulation systems. By addressing any issues promptly, you can prevent energy loss, improve indoor comfort, and extend the lifespan of the insulation, ultimately saving on energy costs and reducing environmental impact.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the key factors in choosing the right exterior wall insulation system, maintaining it effectively, and maximizing energy efficiency can make a significant difference in keeping your space warm and cozy in cold climates.
FAQ Compilation
What is the best material for exterior wall insulation in cold climates?
Common materials like foam board, fiberglass, and mineral wool are often used due to their insulating properties and durability in cold weather conditions.
How often should exterior wall insulation be inspected?
It is recommended to have inspections at least once a year to ensure optimal performance and address any issues promptly.
Can exterior wall insulation help with soundproofing as well?
Yes, certain insulation materials can also contribute to soundproofing your space, providing an added benefit besides thermal insulation.